Predominant Role of the 9-Hydroxy Metabolite of Risperidone in Elevating Blood Prolactin Levels
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The atypical antipsychotic risperidone significantly raises plasma prolactin levels in patients, but clozapine, olanzapine, and quetiapine do not. The differences in neuroendocrine response may be connected with the metabolism of the medications. The authors examined the contributory role of risperidone’s active metabolite 9-hydroxy-risperidone by measuring plasma concentrations of risperidone, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, and prolactin. METHOD: Blood samples taken from 25 patients with psychotic disorders following 6 weeks of treatment with risperidone (mean dose=3 mg/day) were examined. Mean plasma concentrations of risperidone, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, and prolactin were 4.6, 19.4, and 49.3 ng/ml, respectively. RESULTS: The oral dose of risperidone correlated significantly with plasma concentrations of risperidone, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, active moiety, and prolactin. The plasma concentration of 9-hydroxy-risperidone, but not of risperidone, correlated significantly with increases in plasma prolactin. CONCLUSIONS: These data suggest that the 9-hydroxy metabolite plays a predominant role in risperidone’s effect on prolactin release.
The increase in prolactin levels associated with the use of antipsychotics is caused by the blockage of dopamine D2 receptors in the anterior pituitary (1), which is located outside the blood-brain barrier. Most classical antipsychotics are potent D2 receptor antagonists, and, therefore, they induce hyperprolactinemia. Atypical antipsychotic medications are generally less potent D2 receptor antagonists, which is in line with the mild and transient increases in prolactin that have been observed in patients. Risperidone has a moderate potency (2, 3), and yet it produces profound and long-lasting prolactin elevation (4). To date, neither antipsychotics nor their metabolites are known to have any direct effects on serum prolactin levels.
Kapur et al. (1, 5) proposed that, compared with olanzapine and quetiapine, risperidone’s poor penetration of the blood-brain barrier might explain the drug’s greater tendency to cause hyperprolactinemia (1, 5). Risperidone’s metabolite, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, may be a confounding factor. Risperidone is metabolized by CYP2D6 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP3A4 into 9-hydroxy-risperidone. In contrast to the metabolites of most other antipsychotics, 9-hydroxy-risperidone contributes significantly to the therapeutic effect of risperidone (6, 7). We are not aware of any clinical studies that have examined the role of the 9-hydroxy metabolite in the side effects of risperidone. To test the hypothesis that this metabolite contributes considerably to the drug’s tendency to elevate prolactin levels, we measured the plasma levels of risperidone, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, and prolactin in patients who had been treated with risperidone for 6 weeks.
Method
Only patients being treated with risperidone as monotherapy were eligible for inclusion in the study. Blood samples were collected between 8.30 and 9.00 a.m. After liquid-liquid extraction, plasma risperidone and its 9-hydroxy metabolite were measured by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Detection limits of risperidone and the 9-hydroxy metabolite were 2 and 1 ng/ml, respectively. The MAIA clone kit (Ares Serono Diagnostics, Milan, Italy), which enables measurement of prolactin concentrations over a range of 6.0–10,000 ME/liter, was used to measure plasma prolactin levels.
The plasma concentration measurements were normalized by converting them to their natural logarithm. Pearson correlations were calculated, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
Results
The study group consisted of 25 patients (14 male, 11 female; mean age=25 years, SD=7, range=17–52) who had psychotic disorders diagnosed according to DSM-IV criteria (20 patients had diagnoses within the schizophrenia spectrum and five had other psychotic disorders). The mean dose of risperidone was 3 mg/day (range=1–6).
Mean plasma concentrations of risperidone, 9-hydroxy-risperidone, and prolactin were 4.6 ng/ml (SD=1.5), 19.4 ng/ml (SD=3.3), and 49.3 ng/ml (SD=7.2), respectively. Oral risperidone dose was significantly correlated with plasma risperidone levels (r=0.52, N=25, p=0.008), as well as plasma 9-hydroxy-risperidone levels (r=0.57, N=25, p=0.003) and plasma prolactin levels (r=0.45, N=25, p<0.03). In contrast to plasma risperidone, only 9-hydroxy-risperidone was significantly correlated with plasma prolactin levels (r=0.52, N=25, p=0.008). No significant correlations were found between plasma risperidone levels and plasma prolactin levels (r=0.23, N=25, p=0.26) or between plasma risperidone levels and 9-hydroxy-risperidone levels (r=0.29, N=25, p<0.16). Figure 1 shows a scatterplot of the correlations between serum risperidone and 9-hydroxy-risperidone compared with serum prolactin.
Discussion
The degree of hyperprolactinemia observed after 6 weeks of treatment with risperidone was in accordance with previous findings, which have shown prolactin levels exceeding those observed with most classical and atypical antipsychotics (1, 4, 5). Prolactin levels were correlated with levels of the 9-hydroxy metabolite, but not with those of risperidone.
Risperidone is less lipophilic than most antipsychotics, which is reflected by its lower brain-to-plasma ratio (6, 7). The relatively higher peripheral concentration of risperidone might explain the marked transient increase of prolactin, but not the sustained elevation on which it is superimposed (8). To understand this sustained prolactin elevation, the following factors should be considered. Although the potency of risperidone to stimulate prolactin release is comparable to that of 9-hydroxy-risperidone (9), the drug and the metabolite have different pharmacokinetics. The value of 9-hydroxy-risperidone for protein binding (77.4% versus 90.0%) (10) and its partition coefficient (log P: 2.32 versus 3.04) (10) both indicate that the metabolite is less lipophilic than risperidone. Moreover, the half-life of 9-hydroxy-risperidone (20 hours) is much longer than that of risperidone (2–4 hours) (11).
Compared with risperidone, the active metabolite has a similar dopamine D2 receptor affinity, a lower brain-to-plasma ratio, and a longer half-life; these data suggest that 9-hydroxy-risperidone played a predominant role in the strong prolactin elevation that was observed during treatment with risperidone in our study. Arguably, these data also explain risperidone’s high propensity to cause amenorrhea, galactorrhea, and sexual side effects (12).
Received Feb. 2, 2004; revision received April 30, 2004; accepted June 14, 2004. From the Department of Psychiatry, University Hospital Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. Knegtering, Hanzeplein 1, PO Box 30.001, 9700 RB Groningen, the Netherlands; [email protected] or [email protected] (e-mail).
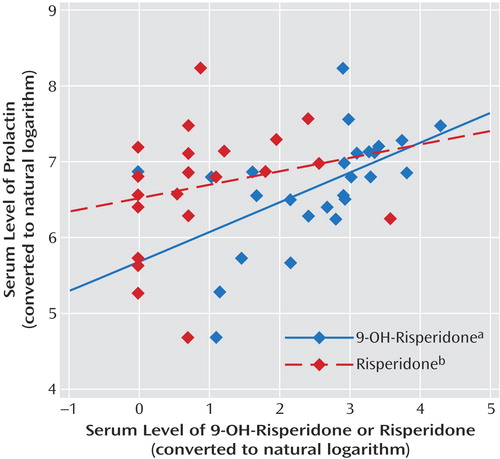
Figure 1. Correlations Between Serum Prolactin Level and 9-Hydroxy-Risperidone or Risperidone in 25 Patients With Psychotic Disorders
ar=0.52, N=25, p=0.008.
br=0.23, N=25, p=0.26.
1. Kapur S, Langois X, Vinken P, Megens AA, Coster de R, Andrews JS: The differential effects of atypical anti-psychotics on prolactin elevation are explained by their differential blood-brain disposition: a pharmacological analysis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002; 302:1129–1134Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
2. Leysen JE: Review of neuroleptic receptors: specificity and multiplicity of in vitro binding related to pharmacological activity in clinical pharmacology, in Psychiatry: Neuroleptic and Antidepressant Research. Edited by Usdin E, Dahl SG, Gram LF, Lingjaerde O. London, Macmillan, 1981, pp 35–62Google Scholar
3. Leysen JE, Janssen PM, Gommeren W, Wynants J, Pauwels PJ, Janssen PA: In vitro and in vivo receptor binding and effects on monoamine turnover in rat brain regions of the novel antipsychotics risperidone and ocaperidone. Mol Pharmacol 1992; 41:494–508Medline, Google Scholar
4. Knegtering H, Lamberts PA, Prakken G, ten Brink C: Serum prolactin levels and sexual dysfunction in antipsychotic medication, such as risperidone: a review. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2000; 12:19–26Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
5. Kapur S, Roy P, Daskalakis J, Remington G, Zipursky R: Increased dopamine D2 receptor occupancy and elevated prolactin level associated with addition of haloperidol to clozapine. Am J Psychiatry 2001; 158:311–314Link, Google Scholar
6. van Beijsterveldt LE, Geerts RJ, Leysen JE, Megens AA, Van den Eynde HM, Meuldermans WE, Heykants JJ: Regional brain distribution of risperidone and its active metabolite 9-hydroxy-risperidone in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994; 114:53–62Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
7. Aravagiri M, Yuwiler A, Marder SR: Distribution after repeated oral administration of different dose levels of risperidone and 9-hydroxy-risperidone in the brain and other tissues of rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1998; 139:346–363Crossref, Google Scholar
8. Turrone P, Kapur S, Seeman MV, Flint AJ: Elevation of prolactin levels by atypical antipsychotics. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159:133–135Link, Google Scholar
9. Bowden CR, Viona SJ, Woestenborghs R, de Coster R, Heykants J: Stimulation by risperidone of rat prolactin secretion in vivo and in cultured pituitary cells in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1992; 262:699–706Medline, Google Scholar
10. Mannens G, Meuldermans W, Snoeck E, Heykants J: Plasma protein binding of risperidone and its distribution in blood. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994; 144:566–572Crossref, Google Scholar
11. Heykants J, Huang ML, Mannens G, Meuldermans W, Snoeck E, van Beijsterveldt LE, van Peer A, Woestenborghs R: The pharmacokinetics of risperidone in humans: a summary. J Clin Psychiatry 1994; 55(suppl):13–17Google Scholar
12. Knegtering H, van der Moolen AEGM, Castelein S, Kluiter H, van den Bosch RJ: What are the effects of antipsychotics on sexual dysfunctions and endocrine functioning? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2003; 22(suppl 2):109–123Google Scholar



