Association Among Visual Hallucinations, Visual Acuity, and Specific Eye Pathologies in Alzheimer’s Disease: Treatment Implications
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Studies suggest a link between visual acuity and visual hallucinations in dementia, but links with specific eye pathologies have not been evaluated. METHOD: Fifty patients (20 with visual hallucinations, 30 without) with probable Alzheimer’s disease had an evaluation of psychotic symptoms. Visual acuity was measured before and after refractions, and ophthalmological examinations included standardized assessments for cataracts and macular degeneration. RESULTS: Impaired visual acuity and the severity of cognitive impairments were significantly associated with visual hallucinations. No patients with normal acuity (6/5 or 6/6 on the Snellen chart) experienced these symptoms. Impaired acuity improved with refraction in 60% (N=12) of the patients with visual hallucinations. Of specific eye pathologies, only cataracts were significantly associated with visual hallucinations. Descriptive follow-up information suggests that an optician’s assessment for glasses improves outcome. CONCLUSIONS: Glasses and cataract surgery need evaluation as prophylactic or adjunctive treatments for visual hallucinations in patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease.
Many (more than 20%) of the patients with Alzheimer’s disease experience visual hallucinations. They are distressing (1), precipitate admission to residential care (1), and are associated with more rapid cognitive decline (2). Reports (1, 3) suggest a link between visual hallucinations and visual impairment, although impaired acuity was inferred from clinical interviews in two studies. This report examines the association among visual hallucinations, acuity, and specific eye pathologies in 50 patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease.
METHOD
Consecutive patients with dementia were included in a case registry. The History and Aetiology Schedule (4) was used for the study; it records psychiatric and past medical history, medication, and the results of a standardized physical examination. Psychotic symptoms were rated with the Columbia University Scale for Psychopathology in Alzheimer’s Disease (5), from which operationalized diagnoses of visual hallucinations, delusions, and delusional misidentification were made (6). An appendix rated the minutes of visual hallucinations over the week before the assessment. Cognitive assessments were made with the cognitive section of the Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly, section B (7). A diagnosis of probable Alzheimer’s disease was made according to the criteria of the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke and the Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association (8).
Postmortem examinations were obtained from 50 of the 338 case registry patients. The positive predictive value for probable Alzheimer’s disease in a clinical setting against a neuropathological diagnosis was 80% (9).
Fifty patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease were selected for ophthalmological evaluation (20 with visual hallucinations, 30 without). Patients and caregivers were shown an information sheet that explained the study in full. If they wished to participate, written consent was obtained from the patient and written assent from the next of kin. Approval was obtained from the relevant ethical committee.
Binocular acuity with existing glasses was measured by the Snellen chart. All patients were refracted by the study optometrist and examined by an ophthalmologist (F.M.C.) who was blind to the subject’s hallucination status. Assessments included the visual field evaluation to confrontation and the slit lamp biomicroscopy before and after pupil dilation. Cataracts were defined by a simplified Oxford cataract grading system (10). Age-related macular degeneration was graded by using photographs from the Wisconsin age-related macular degeneration grading system (11) and scored when visually significant.
Visual acuity and cognitive impairment were compared among patients with and without visual hallucinations by using the Mann-Whitney U test. Cataracts were compared between the two groups by using chi-square analysis. Statistical analyses were made with the SPSS computer software.
RESULTS
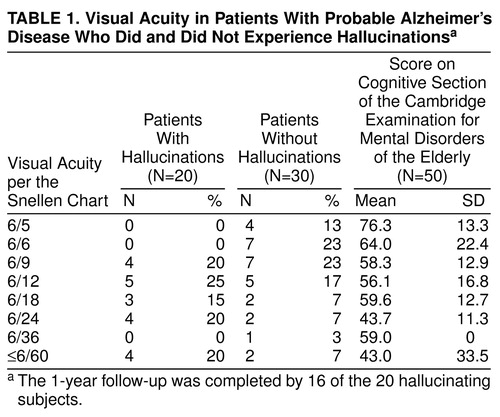
Sixty-two case registry patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease were living at the time of the study. All 20 with visual hallucinations and 30 who were randomly selected from the 42 without hallucinations were enrolled. Mean age at assessment was 81.7 years for hallucinators and 79.2 years for nonhallucinators. Seventeen of the 20 hallucinators were women, compared to 17 of the 30 nonhallucinators (χ2=4.1, df=1, p=0.04). Hallucinators had significantly worse mean scores than nonhallucinators on the cognitive section of the Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly (48.6 and 62.7) (Mann-Whitney U, z=2.6, p=0.009). Visual acuity was also significantly more impaired in hallucinators (Mann-Whitney U, z=3.0, p=0.003) (table 1). No patients with visual hallucinations had normal acuity (6/5 or 6/6 on the Snellen chart).
Hallucinators with a visual acuity of 6/12 or worse had 33.7 minutes of visual hallucinations in the week before the assessment compared to 3.3 minutes for the hallucinators without impaired visual function, and eight of 13 (62%) of the hallucinators with poor visual acuity (6/12 or worse) who completed the follow-up still had visual hallucinations at 1 year compared to one of four (25%) of the hallucinators without impaired visual function.
Delusions were also significantly associated with impaired visual acuity (Mann-Whitney U, z=2.3, p=0.02), and there was a trend toward an association with delusional misidentification (Mann-Whitney U, z=1.8, p=0.06).
Medications likely to influence visual hallucinations or visual acuity were not substantially different in patients with or without visual hallucinations (hallucinators: tricyclic antidepressants=15% [N=3], anticholinergics=5% [N=1], neuroleptics=25% [N=5], steroids=0% [N=0]; nonhallucinators: tricyclic antidepressants=7% [N=2], anticholinergics=7% [N=2], neuroleptics=13% [N=4], steroids=7% [N=2]; no patients were taking tamoxifen, chloroquine, or antituberculosis medications).
Logistic regression analysis examined cognition, visual acuity, and gender as associates of visual hallucinations; only impaired visual acuity (Wald χ2=4.2, df=2, p=0.04) was entered into the equation.
Eye pathology was identified in 13 (65%) of the hallucinators and 13 (43%) of the nonhallucinators. Cataracts (45%, N=9 versus 10%, N=3) were significantly more common among hallucinators (p=0.006, Fisher’s exact test). The rates of glaucoma (hallucinators, 10%, N=2; nonhallucinators, 17%, N=5), macular degeneration (10%, N=2 and 13%, N=4, respectively), and corneal scars (0%, N=0 and 3%, N=1, respectively) were similar. Confrontational visual field evaluations showed one (5%) of the hallucinators had reduction (retinal arterial occlusion), whereas three (10%) of the nonhallucinators had constriction (two with glaucomatous and one with aphakic lenses in their glasses).
Twelve (60%) of the hallucinators had their acuity improved by the refractions. Optician referral was instigated for six patients with visual hallucinations and impaired acuity who were followed up for 1 year. Four of six (67%) of these patients were free of hallucinations at follow-up, compared to only one of six (17%) who had no action taken.
A modest correlation was seen between scores on the cognitive section of the Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly and visual acuity (rs=0.30, N=50, p=0.03); the relationship is illustrated in table 1.
DISCUSSION
An association was demonstrated between visual hallucinations and impaired acuity; visual hallucinations may be more persistent and more severe in patients with these conditions. Furthermore, preliminary information from follow-up examinations indicates that referral to an optician may improve the outcome of visual hallucinations. Of the specific eye pathologies, only cataracts were significantly associated with visual hallucinations. There was some evidence that impaired visual acuity may be associated with other forms of psychosis.
An association was seen between visual acuity and scores on the cognitive section of the Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly. The main variability was between patients with absent impairment and mild impairment of visual acuity who were not experiencing visual hallucinations. Visual acuity was also independently associated with visual hallucinations in a logistic regression analysis.
Cataract treatment and interventions to improve visual acuity may be important adjuncts to antipsychotic therapy in those suffering from dementia and may have a prophylactic role. Controlled trials are indicated.
Received Sept. 1, 1998; revision received Jan. 14, 1999; accepted March 4, 1999From the Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle, United Kingdom; and the Neurochemical Pathology Unit, Medical Research Council, Newcastle General Hospital. Address reprint requests to Dr. Ballard, Neurochemical Pathology Unit, Medical Research Council, Newcastle General Hospital, Newcastle Upon Tyne NE4 6BE, United Kingdom; [email protected] (e-mail)
 |
1. Ballard C, Gray A, Ayre G: Psychotic symptoms in behavioral disturbances in dementia: a review. Rev Neurol (Paris) (in press)Google Scholar
2. Drevets WC, Rubin EH: Psychotic symptoms and the longitudinal course of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Biol Psychiatry 1989; 25:39–48Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
3. Holroyd S, Sheldon-Keller A: A study of visual hallucinations in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 1995; 3:198–205Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
4. Dewey ME, Copeland JRM, Lobo A, Saz P, Dia JL: Computerized diagnosis from a standardized history schedule: a preliminary communication about the organic section of the HAS-AGECAT system. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 1992; 7:443–446Crossref, Google Scholar
5. Devanand DP, Miller L, Marder K, Bell K, Mayeaux R, Stern J: The Columbia University Scale for Psychopathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch Neurol 1992; 49:371–376Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
6. Burns A, Jacoby R, Levy R: Psychiatric phenomena in Alzheimer’s disease. Br J Psychiatry 1990; 157:72–76Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
7. Roth M, Tym E, Mountjoy C, Huppert F, Hendrie H, Verma S, Goddard R: CAMDEX: a standardized instrument for the diagnosis of mental disorder in the elderly with special reference to the early detection of dementia. Br J Psychiatry 1986; 149:698–709Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
8. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984; 34:939–944Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
9. McKeith IG, Ballard CG, Perry RH, Ince PG, Jaros E, Neill D: Predictive accuracy of clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia with Lewy bodies—a prospective neuropathological validation study (abstract). Neurology 1998; 50(suppl 4):181Google Scholar
10. Sparrow JM, Bron AJ, Brown NAP, Ayliffe W, Hill AR: The Oxford clinical cataract classification and grading system. Int Ophthalmol 1986; 9:207–225Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
11. Klein R, Davis MD, Magli YL, Segal P, Klein BEK, Hubbard L: The Wisconsin age-related maculopathy grading system. Ophthalmology 1991; 98:1128–1134Google Scholar



