Auditory Mismatch Negativity in Schizophrenia: Topographic Evaluation With a High-Density Recording Montage
Abstract
Objective: The mismatch negativity, a negative component in the auditory event-related potential, is thought to index automatic processes involved in sensory or echoic memory. The authors’ goal in this study was to examine the topography of auditory mismatch negativity in schizophrenia with a high-density, 64-channel recording montage.Method: Mismatch negativity topography was evaluated in 23 right-handed male patients with schizophrenia who were receiving medication and in 23 nonschizophrenic comparison subjects who were matched in age, handedness, and parental socioeconomic status. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale was used to measure psychiatric symptoms.Results: Mismatch negativity amplitude was reduced in the patients with schizophrenia. They showed a greater left-less-than-right asymmetry than comparison subjects at homotopic electrode pairs near the parietotemporal junction. There were correlations between mismatch negativity amplitude and hallucinations at left frontal electrodes and between mismatch negativity amplitude and passive-apathetic social withdrawal at left and right frontal electrodes. Conclusions: Mismatch negativity was reduced in schizophrenia, especially in the left hemisphere. This finding is consistent with abnormalities of primary or adjacent auditory cortex involved in auditory sensory or echoic memory. Am J Psychiatry 1998; 155: 1281-1284
The mismatch negativity, a negative component in the auditory event-related potential (1), is thought to index automatic processes involved in sensory or echoic memory. Both animal and human studies suggest that the mismatch negativity to deviant auditory stimuli is primarily generated in the auditory cortex, with secondary sources in the adjacent superior temporal gyrus cortex (2).
Mismatch negativity amplitude has been reported to be reduced in medicated (3) and unmedicated (4) patients with schizophrenia. These findings suggest a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia at the level of the auditory sensory cortex, consistent with findings of anatomical abnormalities affecting the superior temporal gyrus in schizophrenia (5, 6). Most of the studies reviewed here used small numbers of electrodes and thus were limited in evaluating mismatch negativity topography (scalp distribution). Javitt et al. (7) reported evidence of a trend-level left-less-than-right asymmetry at temporal electrodes. This asymmetry is of particular interest given studies showing left temporal auditory P300 abnormalities as well as structural left temporal abnormalities on magnetic resonance imagining measures (6, 8).
In the present study, we evaluated auditory mismatch negativity using a 64-channel recording system to clarify the topographic distribution in patients with schizophrenia compared with nonschizophrenic subjects. An exploratory analysis evaluated the correlation of mismatch negativity amplitude with psychiatric symptoms.
METHOD
Twenty-three right-handed male patients with schizophrenia (diagnosed according to DSM-IV criteria) were recruited from the Brockton Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center. All of the patients were receiving neuroleptic medication. Their mean age was 43.6 years (SD=7.9), and their mean neuroleptic dose was 568.9 mg/day (chlorpromazine equivalents). Twenty-three male comparison subjects were recruited who were matched in age (mean=40.2, SD=8.4), handedness, and parental socioeconomic status to the group of patients. Psychiatric symptoms were evaluated with the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (9). After complete description of the study to the subjects, written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Deviant stimuli were 1.2 kHz tones (0.05 probability), and standard stimuli were 1.0 kHz tones, with a total of 1,600 tone presentations. The 100-msec duration tones, with a 300-msec interstimulus interval, were presented binaurally over ETYMOTIC insert headphones at a 75-dB sound pressure level.
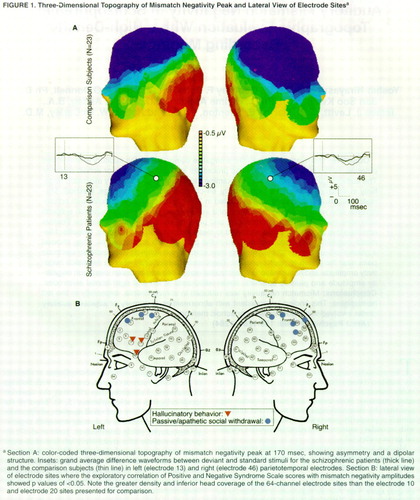
Sixty-four-channel EEG was collected with a Geodesic Sensor Net (Electrical Geodesics, Inc., Eugene, Ore.). To eliminate eye movement and other artifacts, any trial exceeding 75 mV was discarded. Recordings were vertex referenced and later digitally re-referenced to a left mastoid. Mismatch negativity difference waveforms were constructed by subtracting the standard event-related potential from the deviant event-related potential for each subject (figure 1A). Mismatch negativity latency was measured automatically as the most negative peak at midline electrode sites between 100 and 300 msec. Amplitude was measured as the average amplitude between 100 and 200 msec at the 64 electrodes. A nearest neighbor interpolation was used for the construction of three-dimensional maps of the voltage field.
For the three midline electrodes, the mismatch negativity amplitude was analyzed by a two-way mixed analysis of variance (ANOVA) with recording electrode (electrodes 61, 30, and 21) (figure 1A) as a within factor and group (patients with schizophrenia versus comparison subjects) as a between factor. In an analysis of lateral asymmetry in the comparison group, t tests compared mismatch negativity amplitudes at all homotopic left-right electrode pairs. Next, ANOVAs tested for group laterality differences with group (patients with schizophrenia versus comparison subjects) as a between factor and side (left versus right) as a within factor in all homotopic electrode pairs. Exploratory correlational analyses were conducted between mismatch negativity amplitude values at temporal-frontal electrode sites (figure 1B) and the total positive symptom and negative symptom scores from the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale as well as for each positive and negative item. To reduce the number of false positive findings, we report only the correlations that were significant at multiple, contiguous electrode sites.
RESULTS
The mismatch negativity peaked at about 170 msec after stimulus onset (figure 1A). A two-way mixed ANOVA revealed that mismatch negativity amplitude was reduced in patients (F=11.38, df=1, 44, p=0.002) at the three midline electrodes (electrodes 60, 21, and 30). A significant effect of electrode (F=86.30, df=2, 88, p<0.001) indicated a frontal maxima in the mismatch negativity amplitude distribution. Mismatch negativity latency did not differ between groups.
Three-dimensional voltage topographic maps (figure 1) suggest that both groups showed a left-less-than-right mismatch negativity asymmetry; this asymmetry was more pronounced in the temporal-parietal region in the patient group. In the comparison group, t tests showed significant left-less-than-right mismatch negativity amplitudes at two temporal homotopic electrode pairs, electrodes 15 and 47 (t=2.57, df=22, p=0.02) and electrodes 16 and 45 (t=2.12, df=22, p=0.05) (near T3/T4), indicating a right maximal distribution of mismatch negativity. An ANOVA also showed a significant group-by-side interaction at homotopic electrode pair 8 and 34 (F=7.12, df=1, 44, p=0.01) and electrode pair 13 and 46 (F=5.78, df=1, 44, p=0.02) (near C3/C4) as well as at electrodes 20 and 38 (F=5.51, df=1, 44, p=0.02), electrodes 19 and 40 (F=6.12, df=1, 44, p=0.02), and electrodes 18 and 43 (F=4.39, df=1, 44, p=0.04) (near P3/P4). These findings suggest a greater left-less-than-right mismatch negativity asymmetry in schizophrenia.
According to Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale scores, hallucinations were significantly correlated (r>0.45, df=22, p<0.05) with mismatch negativity amplitude at three left frontal electrodes near the temporal lobe (figure 1B). Passive-apathetic social withdrawal was significantly correlated (r>0.42, df=22, p<0.05) at right and left frontal electrodes. These evaluations were exploratory; after Bonferroni corrections, none of these correlations was significant.
DISCUSSION
This study found that mismatch negativity amplitude was reduced in patients at midline electrodes. An analysis of the high-density topography indicated a greater left-less-than-right mismatch negativity asymmetry over the parietotemporal junction in patients with schizophrenia than in nonschizophrenic comparison subjects. Because mismatch negativity likely originates in the primary auditory cortex, or in nearby superior temporal gyrus sites, these findings are consistent with reports of more severe left temporal lobe abnormalities in schizophrenia (10).
The correlations of hallucinations with mismatch negativity amplitude at left (but not right) frontal electrodes that are near the temporal lobe may reflect contributions of superior temporal gyrus sources. It is possible that the midline and bilateral mismatch negativity amplitude correlations with social withdrawal may reflect frontal lobe contributions; mismatch negativity is known to be reduced in patients with frontal lobe abnormalities (11), which have also been implicated in negative symptoms (1-).
Received Oct. 27, 1997; revision received March 13, 1998; accepted April 8, 1998. From the Department of Psychiatry at the Clinical Neuroscience Division, Laboratory of Neuroscience, Harvard Medical School, Brockton VA Medical Center.. Address reprint requests to Dr. McCarley, Department of Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Brockton VA Medical Center, Psychiatry (116A), 940 Belmont St., Brockton, MA 02401; [email protected] (e-mail). Supported by NIMH grant MH-40799 (Dr. McCarley), by the Department of Veterans Affairs Schizophrenia Center (Dr. McCarley), and by NIMH grants MH-01110 and MH-50747 (Dr. Shenton).
1. Naatanen R, Gaillard AW, Mantysalo S: Early selective-attention effect on evoked potential reinterpreted. Acta Psychol 1978; 42:313–329Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
2. Alho K: Cerebral generators of mismatch negativity (MMN) and its magnetic counterpart (MMNm) elicited by sound changes. Ear Hearing 1995; 16:38–51Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
3. Shelley AM, Ward PB, Catts SV, Michie PT, Andrews S, McConaghy N: Mismatch negativity: an index of a preattentive processing deficit in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 1991; 30:1059–1062Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
4. Javitt DC, Doneshka P, Grochowski S, Ritter W: Impaired mismatch negativity generation reflects widespread dysfunction of working memory in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1995; 52:550–558Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
5. Barta PE, Pearlson GD, Powers RE, Richards SS, Tune LE: Auditory hallucinations and smaller superior temporal gyrus volume in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 1990; 147:1457–1462Link, Google Scholar
6. Shenton ME, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, Pollak SD, LeMay M, Wible CG, Hokama H, Martin J, Metcalf D, Coleman M, McCarley RW: Abnormalities of the left temporal lobe and thought disorder in schizophrenia: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. N Engl J Med 1992; 327:604–612Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
7. Javitt DC, Doneshka P, Zylberman I, Ritter W, Vaughan HG Jr: Impairment of early cortical processing in schizophrenia: an event-related potential confirmation study. Biol Psychiatry 1993; 33:513–519Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
8. McCarley RW, Shenton ME, O"Donnell BF, Faux SF, Kikinis R, Nestor PG, Jolesz FA: Auditory P300 abnormalities and left posterior superior temporal gyrus volume reduction in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50:190–197Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
9. Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA: The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987; 13:261–276Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
10. Shenton ME, Wible CG, McCarley RW: A review of magnetic resonance imaging studies of brain abnormalities in schizophrenia, in Brain Imaging in Clinical Psychiatry. Edited by Krishnan KRR, Doraiswamy PM. New York, Marcel Dekker, 1997, pp 297–380Google Scholar
11. Alho K, Woods DL, Algazi A, Knight RT, Naatanen R: Lesions of frontal cortex diminish the auditory mismatch negativity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1994; 91:353–362Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar



